How to review timesheets & prepare invoices
This article talks about preparing invoices using a timesheet.

1. Introduction
A timesheet is a structured document—typically in Excel or digital format—used to systematically track the number of hours a resource (employee or contractor) spends on assigned tasks or projects over a specific period (e.g., daily, weekly, or monthly). Timesheets are critical in determining work effort, calculating billable hours, and generating accurate invoices for client billing
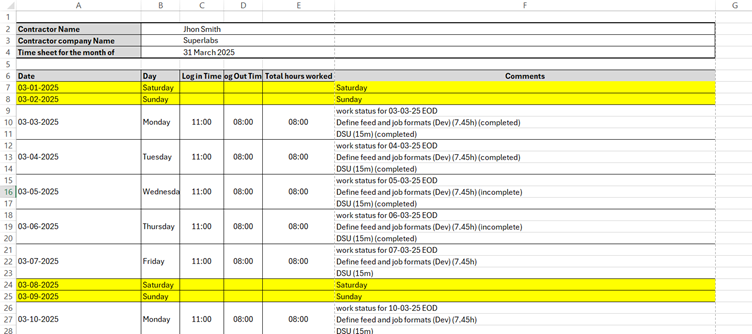
2. Timesheet Structure and Creation
Each resource is allocated a dedicated Excel workbook, containing individual sheets for each month (e.g., "Jan 2025", "Feb 2025", etc.).
2.1. Timesheet Columns Description
Each monthly sheet must contain the following columns:
|
Column Name |
Description |
|
Date |
The calendar date of the working
day (e.g., 01-May-2025). |
|
Day |
The name of the weekday (e.g.,
Monday, Tuesday, etc.). |
|
Log In Time |
Time at which the resource
started work for the day. |
|
Log Out Time |
Time at which the resource
concluded work for the day. |
|
Total Hours Worked |
Computed as: Log Out Time −
Login Time (excluding unpaid breaks, if any). |
|
Comments |
Short description of work
performed that day (e.g., “Developed login module”). |
2.2. Non-Working Days
- Weekends: Saturdays and Sundays are considered non-working days by default.
- Leave Days: Public holidays and approved leaves (e.g., sick leave, casual leave) are also marked as non-working days. These should be appropriately annotated in the comments section (e.g., “Sick Leave – Paid”).
- Paid Leaves: If the company policy provides paid leave (e.g., paid sick leave), mark these days accordingly but exclude them from actual billable work hours unless otherwise agreed with the client.
3. Timesheet Review and Approval
- Daily/Weekly Monitoring: Project managers or HR personnel should review timesheets regularly to ensure accuracy and compliance.
- Verification Points: Confirm login/logout accuracy, match task descriptions with assigned duties, and verify working hours.
- Authorization: Timesheets must be signed off (digitally or physically) before proceeding to billing.
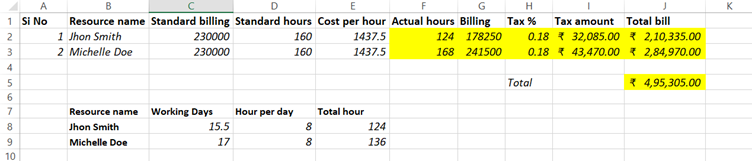
4. Invoice Calculation Sheet.
The invoice calculation is performed using a structured billing table derived from employee timesheets. This sheet typically comprises two main tables:
4.1. Table 1: Billing Summary Per Resource
|
Column Name |
Description |
||
|
Serial No |
|
||
|
Resource
Name |
Full name of
the resource/contractor. |
||
|
Standard
Billing |
Agreed
billing amount for the full standard work month. |
||
|
Standard
Work Hours |
Total
expected work hours for the month (e.g., 160 hours). |
||
|
Cost Per
Hour |
Derived as:
Standard Billing / Standard Work Hours. |
||
|
Actual
Work Hours |
Total number
of hours worked as per the approved timesheet. |
||
|
Billing
Amount |
Actual Work
Hours × Cost Per Hour |
||
|
Tax |
Tax
calculated based on applicable GST structure (IGST/CGST + SGST). |
||
|
Total
Amount |
|
Formula Examples:
- Cost Per Hour = ₹80,000 / 160 = ₹500/hour
- Billing Amount = 140 hours × ₹500 = ₹70,000
- Tax (18%) = ₹70,000 × 0.18 = ₹12,600
- Total Bill = ₹70,000 + ₹12,600 = ₹82,600
4.2. Table 2: Monthly Work Schedule Overview
This table provides a quick view of:
- Number of working days in the month.
- Expected hours per day.
- Total standard hours for the month.
- Actual hours worked per resource.
This helps in validating proportional billing for partial months or deviations from full-time hours.
5. Taxation Guidelines (India-specific GST)
The applicable GST structure depends on the location of the company and the client:
5.1. CGST + SGST (Intra-State Transactions)
- When Applied: The Company and client are in the same state.
- Collected By: Central (CGST) and State Government (SGST).
- Rate Split: Typically, 9% CGST + 9% SGST = 18% total.
Example: Pune (Maharashtra) to Mumbai (Maharashtra): 9% CGST + 9% SGST
5.2. IGST (Inter-State Transactions)
- When Applied: The Company and client are in different states.
- Collected by: Central Government, redistributed to the destination state.
- Rate: Equal to the total GST (e.g., 18%).
Example: Pune (Maharashtra) to Bangalore (Karnataka): 18% IGST
Note:
Tax rates may vary based on service category and current government policies. Always verify with the latest GST schedule or consult a tax advisor.
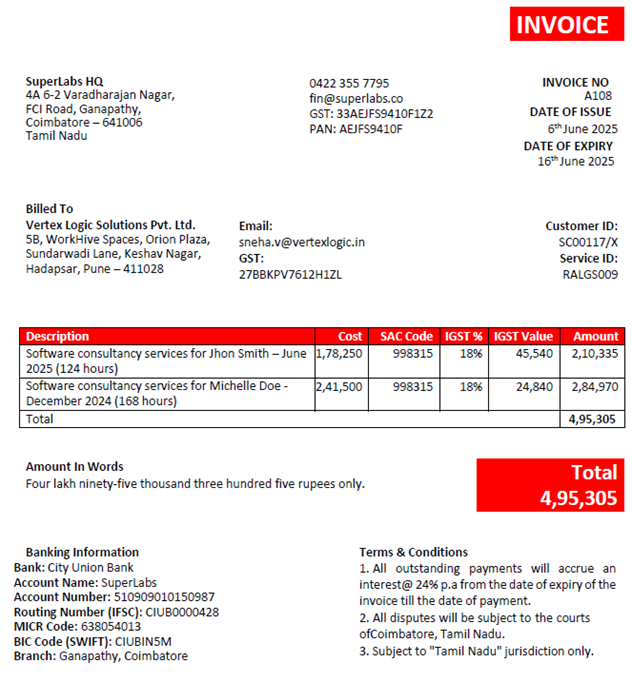
6. Fill Out the Invoice Template
|
Field |
Action |
|
INVOICE NO |
Increment
logically from the last invoice (e.g., i027) |
|
DATE OF
ISSUE |
Current invoice
creation date |
|
DATE OF
EXPIRY |
Add 10 days or
as per terms (e.g., 16th May 2025) |
|
Billed To |
Client name +
address from their records |
|
Customer ID
/ Service ID |
Reference IDs
from the contract |
|
Description |
Mention:
resource name, hours, and month clearly |
|
Cost |
From Step 2 |
|
SAC Code |
Use 998315 (IT Consulting) |
|
IGST % /
Value |
18% / computed
tax |
|
Amount |
Cost + Tax |
|
Total |
Sum of all line
items (₹4,95,305 in your example) |
|
Amount in
Words |
Convert to
words |
|
Bank Info |
Always verify
and update the latest bank details |
|
Terms |
Keep standard
legal terms about interest/jurisdiction |
Invoice Template:
6. Best Practices
- Maintain consistent time formatting
- Protect approved timesheets with read-only settings to prevent accidental changes.
- Maintain audit trails: Save approved versions of timesheets and billing sheets for reference.
- Reconcile invoices monthly with project deliverables and work logs to ensure alignment.




