Guidelines for Preparing a Payment, Receipt, and Overhead Report.

1. General Preparation Steps
Before creating any report, follow these steps:
- Collect all transactions for the relevant period (e.g., a month).
- Organize data by columns: Date, Particulars, Cheque No (if any), Debit, Credit, Balance..
- Identify transaction types using keywords in the "Particulars" column (e.g., "TO NEFT" = payment, "BY NEFT" = receipt).
A. Payments Report
A.1. Purpose:
To track outflows of money from the account — expenses, salaries, purchases, etc.
A.2. Steps to Create:
- Filter transactions where the Debit column has an amount.
- Record:
- Date
- Particular/Payee
- Amount
- Purpose/Category
- Total all payment amounts at the bottom.
A.3. Example:
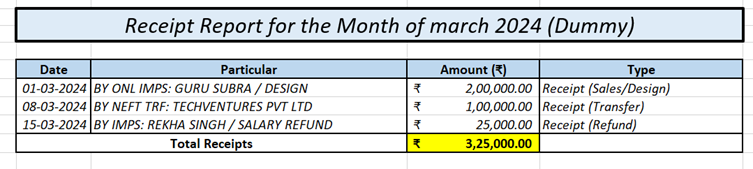
B. Receipts Report
B.1. Purpose:
To track inflows of money into the account — income, refunds, capital injections.
B.2. Steps to Create:
- Filter transactions where Credit column has an amount.
- Record:
- Date
- Source/From
- Amount
- Nature of Receipt (e.g. Sales, Refund, Capital)
- Total all receipts at the bottom.
B.3. Example:
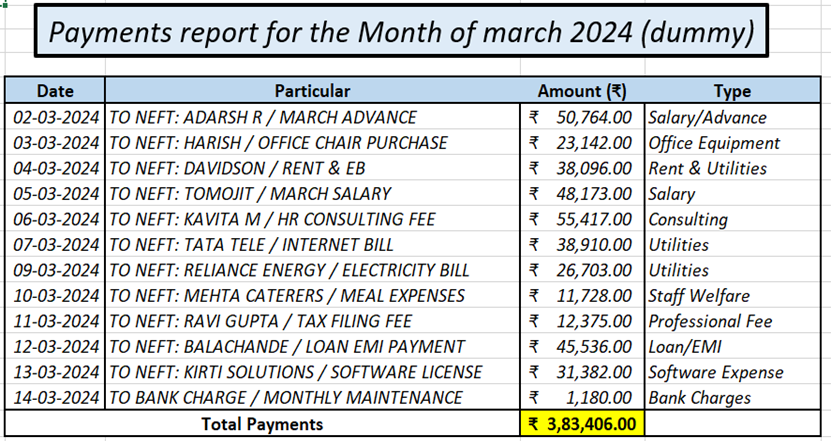
C. Overheads Report
C.1. Purpose:
To list indirect operational expenses — costs not directly tied to production but essential for running the business.
C.2. Steps to Create:
- From the Payments Report, identify non-core operational expenses such as:
- Rent
- Utilities
- Office supplies
- Professional fees
- Salaries (admin, HR)
- Software, Bank fees, Loan EMIs
- Group each payment by Overhead Category. The following are the common overhead categories.
- Rent
- Utilities
- Office supplies
- Taxes
- Depreciation on fixed assets
- Advertising expenses
- Permits and licenses
- Accounting and legal fees
- Record:
- Date
- Description
- Amount
- Overhead Type
C.3. Example:
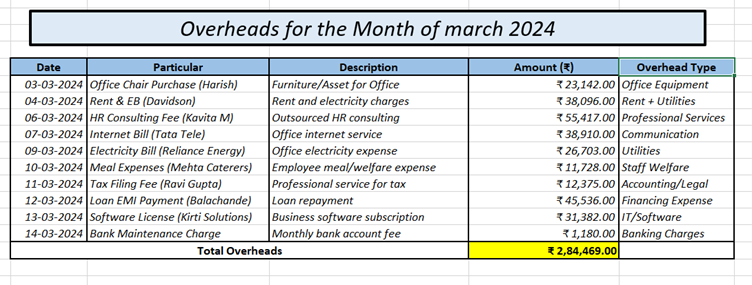
Best Practices
- Use Excel or Google Sheets for sorting and filtering.
- Use consistent naming for categories (e.g., "Utilities", "Payroll").
- Double-check debit/credit alignment before generating the report.
- Maintain backups and create monthly folders for organized storage.




